Mitigation, adaptation and regulation strategies against sea level rise in coastal cities- Technology News, DD FreedishNews
Kamlesh GadeNov 02, 2020 17:29:41 IST
Editor’s Note: This story is part of a campaign called Biodiversity by the Bay, run by Mumbai’s Ministry of Magic. The campaign is a citizen-driven environmental initiative to protect the rich biodiversity that lives in, or makes a stop in Mumbai on its migratory path elsewhere. The story is the sixth in a series – An architecture student’s vision for building a greener Mumbai – in which young architecture and urban planning students pen down their ideas for a sustainable future for development in Mumbai.
This article explores the reciprocity of the effects of climate change driven sea level rise and urbanism; while seeking out urban design as a tool of mitigating such effects at various scales in Indian urban environments. Climate change has proven to be an anthropogenic process i.e. driven by human activity. Through urban design and its human centric approach, one can find meaningful manifestations of our urban lives that can work in harmonic balance with the ecological systems and processes.
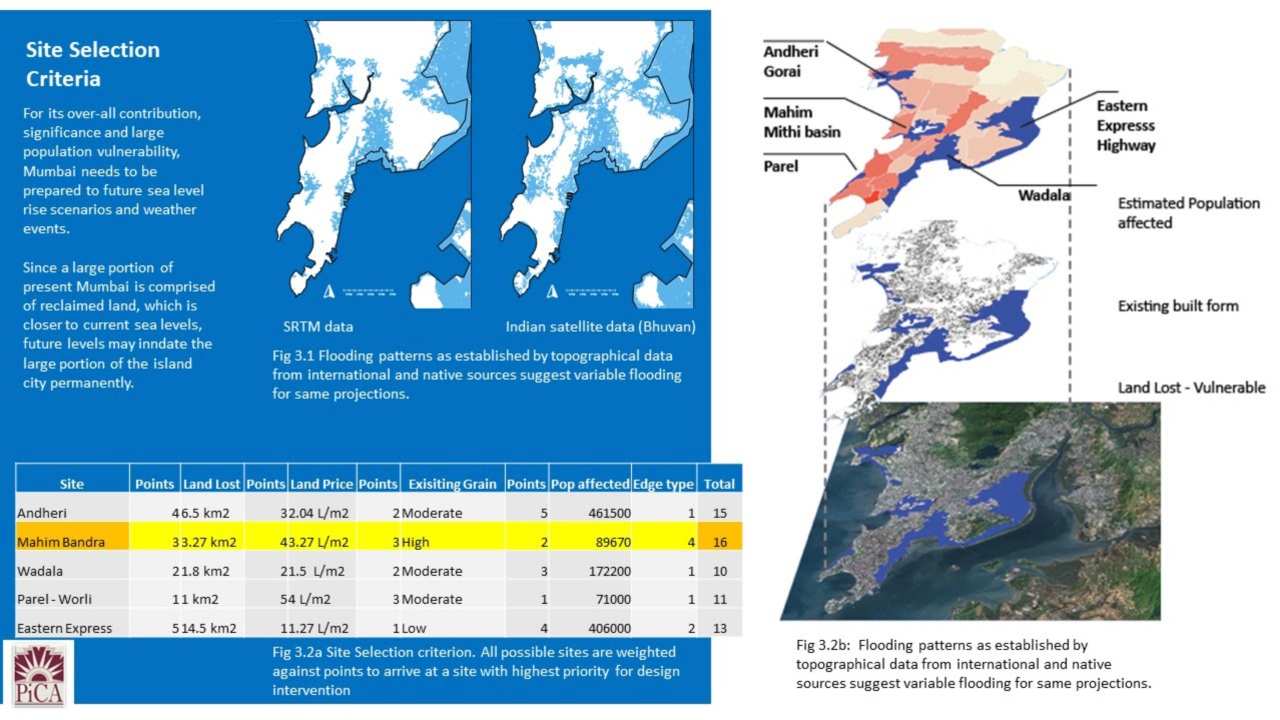
Map showing flooded areas of Mumbai and site selection criteria. Image: Author provided
Urban Design as a tool is explored by studying the existing urban fabric of the site with parameters like open space, public realm, cultural demographics etc. This study overlaid with the understanding of the various factors leading to sea level rise will help in an efficient restructuring of the public realm to devise a design that in conjunction with larger engineering and ecological interventions will sufficiently offset the impacts of sea level rise while laying a model for the future of the urban structure in the city.
Sea level rise analysis and data collection
Table of Contents
This article takes account of data and predictions furnished by the Intergovernmental Panel for Climate Change (IPCC), a body of the United Nations. Additionally, similar climate change research organization data and topographical data in GIS is used to create simulation models and timelines for Sea Level Rise for the city of Mumbai. These models and simulations help in establishing an ideal site for intervention within the city that not only acts as an ideal mix of interactions between land and sea, but also potential benefits of preservation of culture, land and human activities. The second section of the articles focuses on methods of technological and ecological strategies as prescribed by various climate change organizations as well as case studies of such projects by leading nations in the race against sea level rise.
Based on Earth System Models, there is great probability that the feedback between climate change and the carbon cycle will exacerbate global warming. The higher amount of carbon gases in the atmosphere will also lead to acidification of the oceans. The decrease in surface ocean pH is in the range of 0.06 to 0.07 (15 to 17% increase in acidity). There is also a projected decrease in dissolved oxygen in the ocean water. All of these effects not only destroy existing biodiversity but also makes it difficult for marine organisms to thrive.
My Vision for Mumbai’s Green Recovery
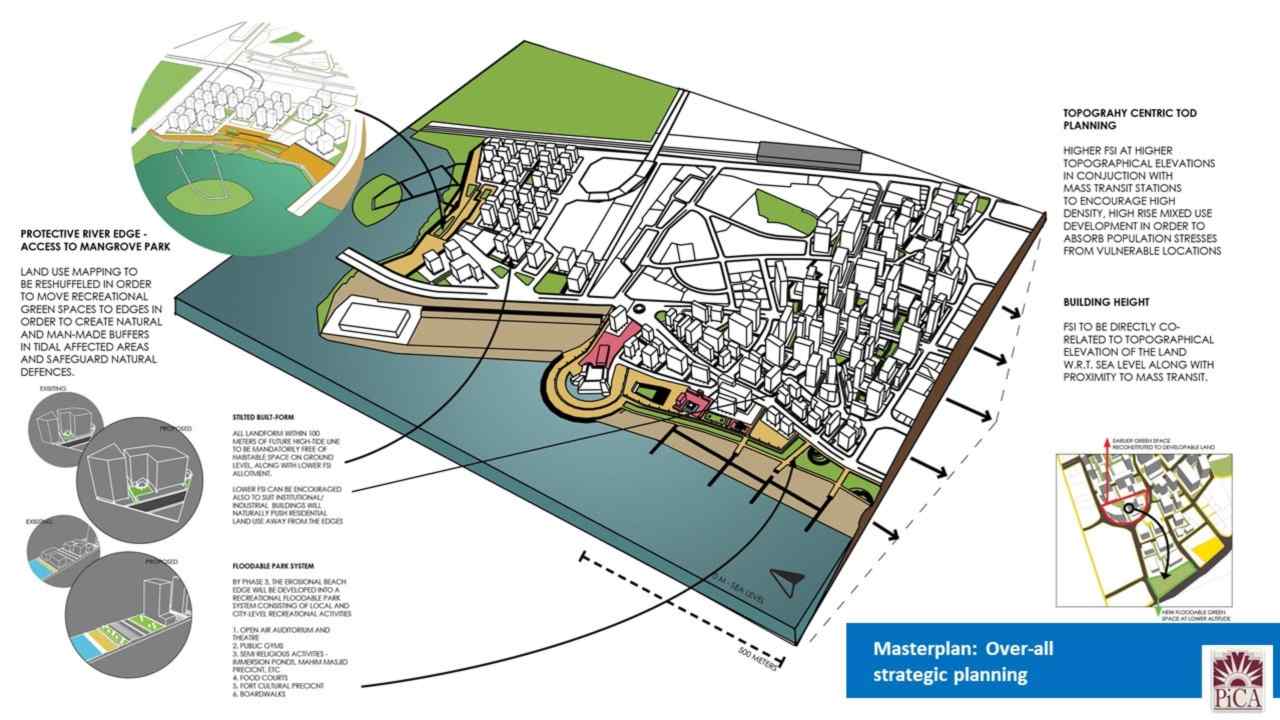
Overall strategic planning. Image: Author provided
The region around Mahim was considered as it accommodates a mixed environment of various land-sea interactions, like beach, promenade, river delta, and various rocky outcrops. The specific effect of sea level rise on the site will cause erosion at the beach edge along with loss of mangroves adjacent to the Mithi river.
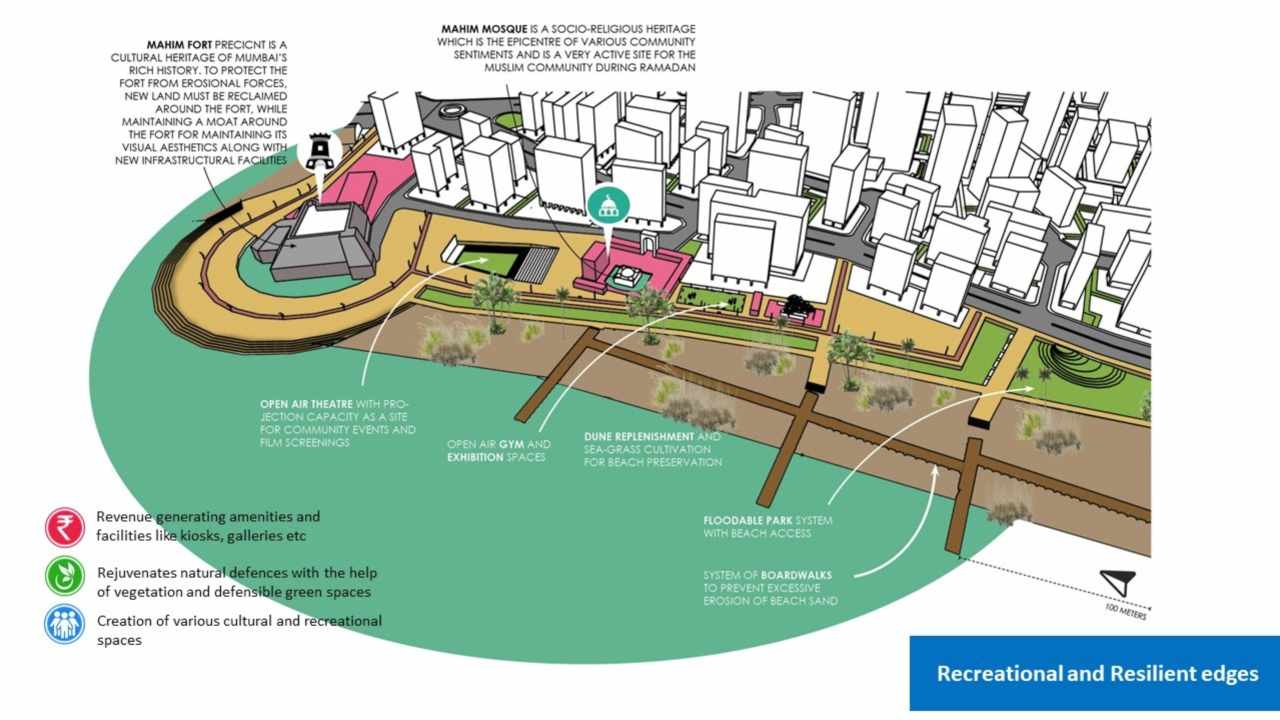
Recreational and resilient edges. Image: Author provided
Therefore, the design vision focuses on the creation of social infrastructure that allows for enjoyment as well as preservation of these ecological features, reintroduction of native vegetation to protect while creating resilient protective social spaces that will over time absorb the damaging effects of rare weather events and gradual sea level rise.
The author is an architect and educator at Pillai HOC College of Architecture. He is currently completing his Master’s thesis in Urban Design from Pillai College of Architecture. Gade is among a group of young architecture and planning students who have shared his ideas on sustainable development for Mumbai for the Ministry of Mumbai’s Magic.
This story has been reproduced with permission from the MMM’s blog. Read the original article here.
#Mitigation #adaptation #regulation #strategies #sea #level #rise #coastal #cities #Technology #News #DD FreedishNews












